What is the Role of Epidemiology in Nursing? A Simple Guide
Introduction of epideiology
- Etymology: From Greek — “epi” (among), “demos” (people), “logos” (study).
- Father of Modern Epidemiology: John Snow, who studied the 1854 cholera outbreak in London.
- Institute Mentioned: National Institute of Epidemiology – Chennai.
Definition
“Study of the distribution and determinants of disease frequency in man.” — MacMahon (1960)
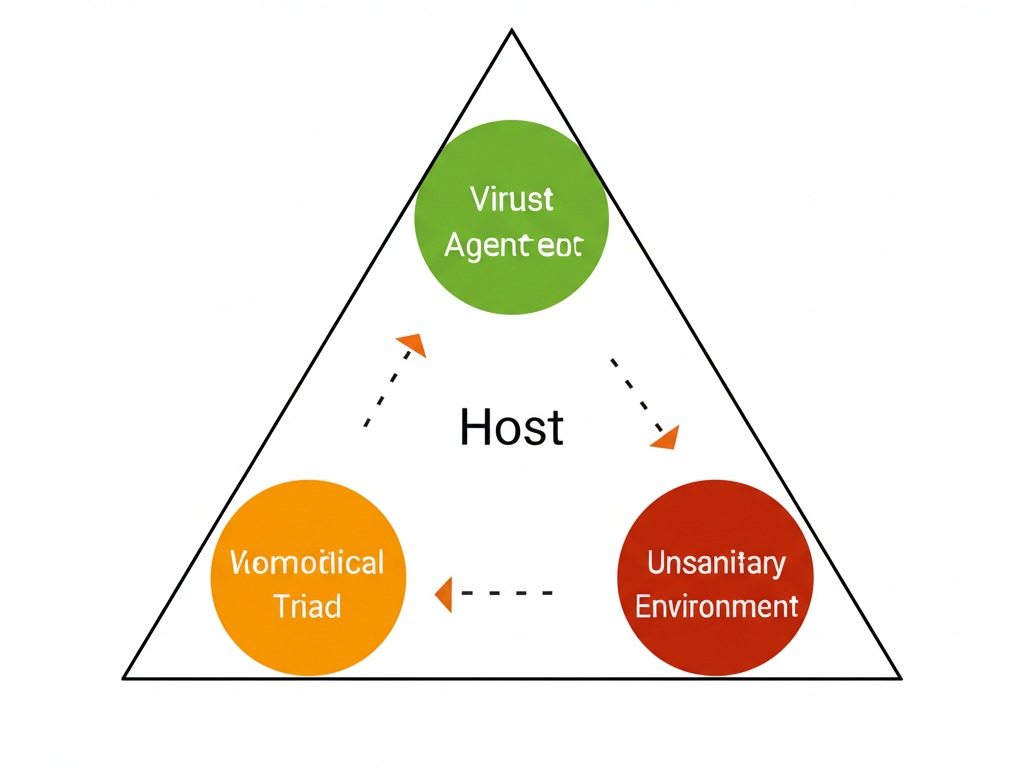
Epidemiological Triad
Used to explain infectious disease transmission:
- Agent – e.g., virus, bacteria (Plasmodium in malaria)
- Host – the human who gets sick
- Environment – e.g., stagnant water (mosquito breeding site)
Objectives of Epidemiology
- Identify disease causes
- Study disease patterns (who, where, when)
- Find risk factors
- Evaluate prevention/control methods
- Provide data for health planning
Types of Epidemiological Studies
1. Descriptive Study
- Describes “who, where, when”
- Example: Diarrhea in children in a village in July
2. Analytical Study
- Finds cause/reason by comparing groups
A. Case-Control Study
- Type: Observational, retrospective
- Groups: Cases (with disease) vs Controls (without)
- Purpose: To find associations between exposure & disease
- Steps:
- Define case
- Select controls
- Match variables
- Assess exposure
- Analyze data
- Calculate Odds Ratio (OR)
OR Interpretation:
- OR > 1: Risk factor present
- OR < 1: Protective factor
- OR = 1: No association
Advantages:
- Good for rare diseases
- Cost & time efficient
Disadvantages:
- Recall & selection bias
- Can’t calculate incidence
- Temporal ambiguity
Example: Smoking and lung cancer
B. Cohort Study
- Starts with healthy people only
- Follow exposed vs unexposed groups over time
- Prospective study
- Example: Follow smokers and non-smokers for 10 years
C. Cross-Sectional Study
- Snapshot at one time
- Checks current disease status and risk factors
- Example: Survey for high BP and diet habits
3. Experimental (Interventional) Study
- Intervention is applied (e.g., new vaccine vs placebo)
- Often in clinical trials


2 Comments