Central Nerve System (CNS): simplified to easy learning
Here are you know detailed and easy to understand notes of central nerve system (CNS).
What is CNS?
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system and main functioning part of the brain. It consists of the brain and spinal cord. It is responsible for sensory data coordination and motor command. The central nervous system act as the primary control centre for the body function and responses.
Types of CNS
- brain
- Spinal cord
- Brain-
- The brain is located in the skull and protected by the cranium cavity of the brain.
- The average weight of the brain is 1400 gm or around 1/50 gm of the body weight.
- The major part of the brain is cerebrum, Cerebellum, brainstem.
The cerebrum
- Cerebrum is the longest part of the Brain.
- Cerebrum is consisting of the right and left hemisphere of the brain.
- Right and left hemishphere is seprated by the fold of dura mater which is called “flex cerebrai“.
- A structure called Corpus callosum is connecting right and left hemisphere of the brain.
- The brain or cerebrum is consisting of gyri (a ridge on the cerebral cortex) and sulci (grooves) that increase the surface area of the brain.
How many Lobes in brain ?
The Cerebrum has 4 lobes in the brain which is as follows-
- Frontal lobe
- Parietal lobe
- Temporal lobe
- Occipital lobe
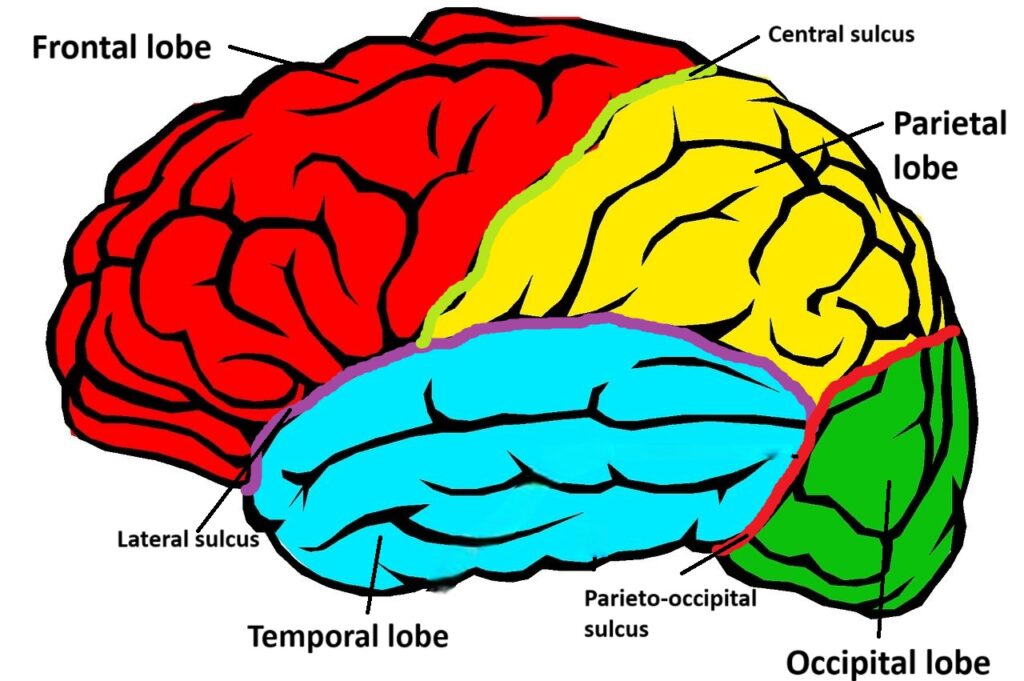
- Frontal lobe-
- It is located in front side of the brain.
- It separated parietal lobe by a sulcus known as “central sulcus” (also known as Rolando sulcus)
- It separated Temporal lobe by a sulcus known as “Lateral sulcus” (also known as Sylvian sulcus)
Frontal lobe functions-
- Motor activity (Movement)
- Attension
- Problem solving skills
- Organizing the matarials
- Consciousness
- Planning
- Behaviour
- social skills
- Personality
- Speech (Broca’s area)
- Parietal lobe-
- It is located between the Frontal and Occipital lobe of the brain.
- It separated Frontal lobe by a sulcus known as “central sulcus” (also known as Rolando sulcus)
- It separated Temporal lobe by a sulcus known as “Lateral sulcus” (also known as Sylvian sulcus)
- It separated Occipital lobe by a sulcus known as “Parieto-occipital sulcus“.
Parietal lobe functions-
- Sensory perception (Touch, Temperature, Pain)
- Spatial awareness (e.g. manner of sitting, dressing code etc)
- coordination
- Spelling
- Understanding language (reading, writing)
- Manipulating objects
- Temporal lobes are located just beneath the Frontal and parietal lobes near of the ear.
- It is divided by both the Frontal and parietal lobes by a sulcus known as “Lateral sulcus” (also known as Sylvian sulcus)
- It separated Occipital lobe by a sulcus known as “Parieto-occipital sulcus“.
Temporal lobe functions-
- Memory
- Language (Wernicke’s area)
- Recognition of face
- Occipital lobe-
- It is located in the posterior side of the brain.
- It separated Occipital lobe and Temporal lobe by a sulcus known as “Parieto-occipital sulcus“.
Occipital lobe functions-
- Vision
- visual interpretation
What are Functions of cerebrum ?
Mainly the cerebrum has three major functions which are as follows-
- Mental functions
- Sensory function
- Motor function
- Mental functions-
- Premotor area-
- premotor area situated in the frontal lobeI.
- It helps in the Motor learning (playing an instrument), Coordination, Learning activity, Movement planning etc.
- Pre-frontal area-
- Prefrontal area is situated in frontal lobe.
- It controls the Decision-Making, planning and problem-solving skills, Emotional regulation etc.
- It also controlled Memory and intelligency.
- Right prefrontal area control- Intelligency.
- Left prefrontal area control- Memory.
- Parietooccipital area-
- Parietooccipital area situated between the parietal and occipital lobe.
- Parietooccipital area Responsible for the understanding of written languages and Motion perception.
- Wernick’s area-
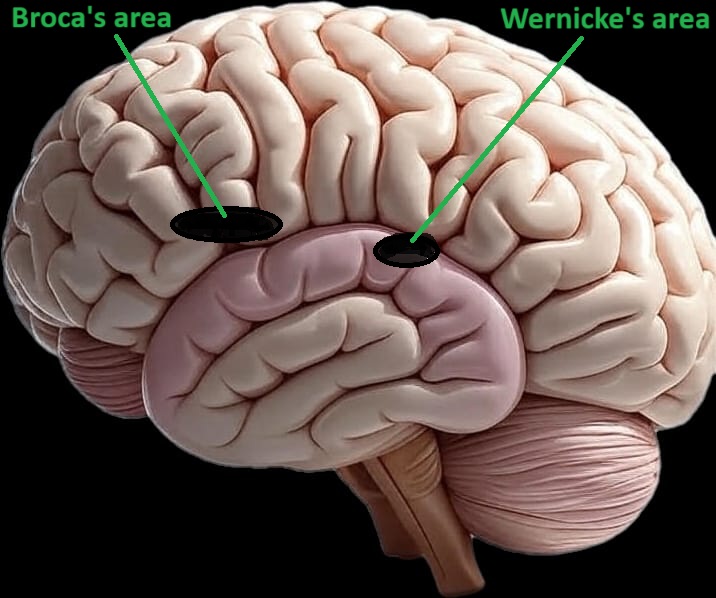
- In the CNS Wernick’s area Situated in the temporal lobe.
- Wernick’s area Responsible for the understanding of verbal languages.
- Sensory Functions-
- Olfactory area-
- In the CNS Olfactory area Situated in the Temporal lobe.
- Olfactory area are responsible for the sense of smell.
- Cranial Nerve- 8th (Olfactory nerve)
- Visual area-
- Visual area is situated in the occipital lobe.
- Primary visual cortex (V1)-
- Location- Occipital lobe.
- Receive visual signals like Light, shape, motion from the eye.
- Secondary visual areas (V2, V3, V4, V5)-
- Location- Around the primary visual cortex.
- Interpret the color, movement, depth etc.
- Taste area-
- In the CNS the Taste area is situated in the parietal lobe.
- Nerve supply-
- 2/3rd part of the tongue- Facial nerve (7th CN).
- 1/3rd part of the tongue- Glossopharyngeal nerve (9th CN).
- Somatosensory area-
- Somatosensory area is situated in the postcentral gyrus of the Parietal lobe.
- It helps to receive the impulses like pain, pressure, touch, vibrations, temperature, sense of the body position etc.
| Parts | Functions |
|---|---|
| Primary Somatosensory cortex (S1) | Main area for receiving touch, pressure, pain, and temperature sensations and It is located in postcentral gyrus. |
| Secondary Somatosensory Cortex (S2) | Helps in more complex interpretation of sensations (texture, shape). Located below the primary cortex. |
| Somatosensory Association Area | Interprets sensory inputs and helps in recognizing objects by touch (stereognosis). Found in Brodmann areas 5 & 7. |
- Motor functions-
- Motor function control centre is situated in the Frontal lobe.
- Motor function helps to perform all motor/ voluntary function in the CNS.
The motor functions have following areas-
- Primary motor area-
- Location- precentral gyrus which is present just in front of the Central sulcus.
- It controls all voluntary muscles of the body except the speech muscles.
- Motor area has specialized cell which called “Betz cell”. These Betz cell controls the extremities of the body.
- The estimated Betz cell is around 25000 to 40000 per hemisphere.
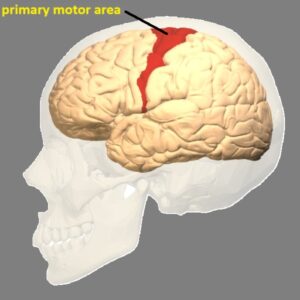
- Supplementary motor area (SMA) –
- It is located in the medial side of the frontal lobe of the CNS.
- It helps in the coordination of the complex movement like clapping.
- Premotor cortex-
- It is located in the in front side of the primary motor cortex.
- The main function the Premotor cortex is making plan and skill movements like typing.
- Broca’s area-
- It is located in the frontal lobe of the CNS.
- It is helping in the controlling of the speech muscles.
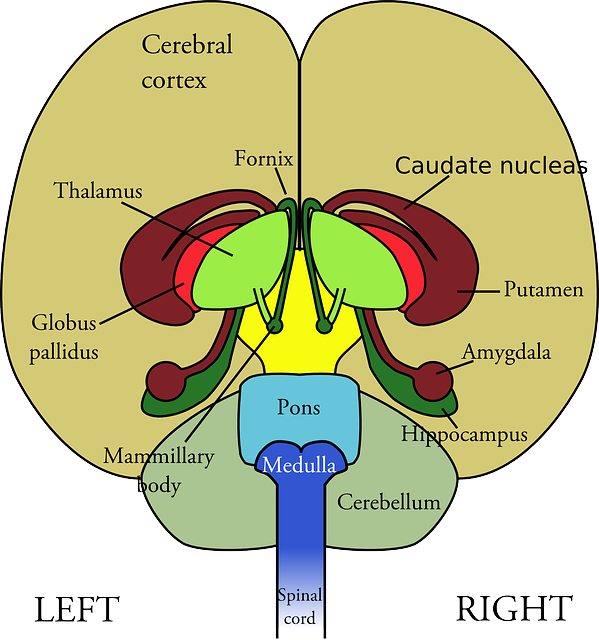
What is Basal ganglia/ Basal nuclei ?
Basal ganglia are the group of interconnected nuclei or cluster of neurons located deep in the central hemisphere. Basal ganglia also known as “Basal Nuclei“. Basal ganglia play a important role in the CNS is controlling voluntary movements, learning, routine behaviors (habits), and emotions.
Main Components of Basal Ganglia:
| Structure | Functions |
| Caudate nucleus | Involved in motor control, learning, and memory |
| Putamen | Works with caudate in controlling movement |
| Globus pallidus | Regulates voluntary movement (internal & external segments) |
| Subthalamic nucleus | Modulates motor output |
| Substantia nigra | Contains dopamine-producing cells; essential for movement control |
Putamen + Caudate nucleus = Striatum
Globus pallidus (internal & external) = Pallidum
Substantia nigra has 2 parts:
- Pars compacta (dopamine source)
- Pars reticulata (output area)
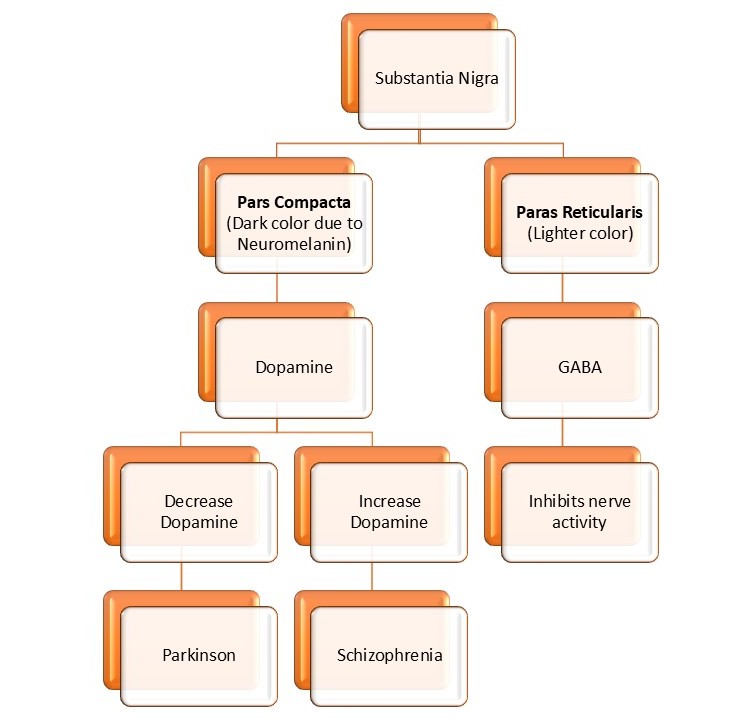
Function of basal ganglia-
- Motor control-
- Regulations of voluntry muscles movements
- helps in coordination
- Eye movement regulation
- cognetive and emotional responses
- learning and habit
- Hand swing during walk
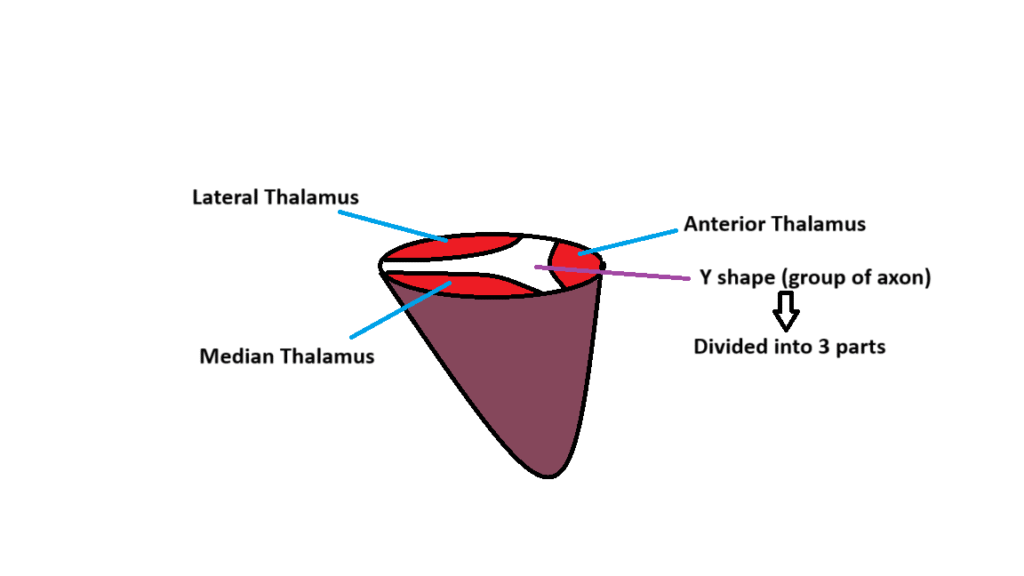
What is Thalamus ?
Thalamus is a part of diencephalon. thalamus is a group of cell body surrended by white matter in the CNS.
Thalamus is also known as the “Relay station” for the sensory and motor nerve.
Thalamus is located just above the brainstem between the cerebral cortex and midbrain.
The shape of the Thalamus is like “walnut”.
The size of the thalamus is 5-7 cm.
Functions-
- Act as the relay station.
- Regulation of the counciousness and alertness.
- Pain perception.
- Motor coordinations