PNEUMOTHORAX: way to prevent emergency
PNEUMOTHORAX
What is Pneumothorax?
Pneumothorax is a collection of air in the pleural space, between the lung and chest wall. It is an medical emergency condition.
Anatomy
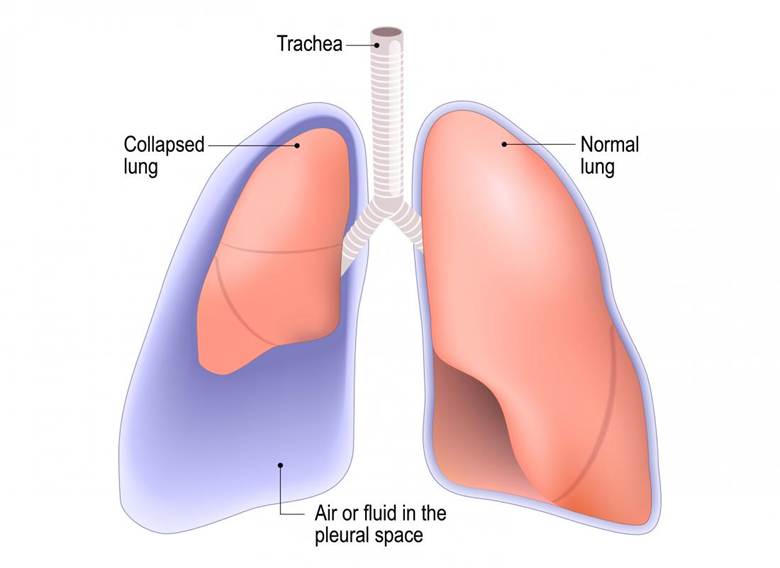
Normal Situation:
- Pleural space has negative pressure
- Lung stays expanded
In Pneumothorax:
- Air enters pleural space
- Pressure increases
- Lung collapses partially or completely
Rememberable point- Problem is ventilation, not oxygen supply.
Types of Pneumothoraxes
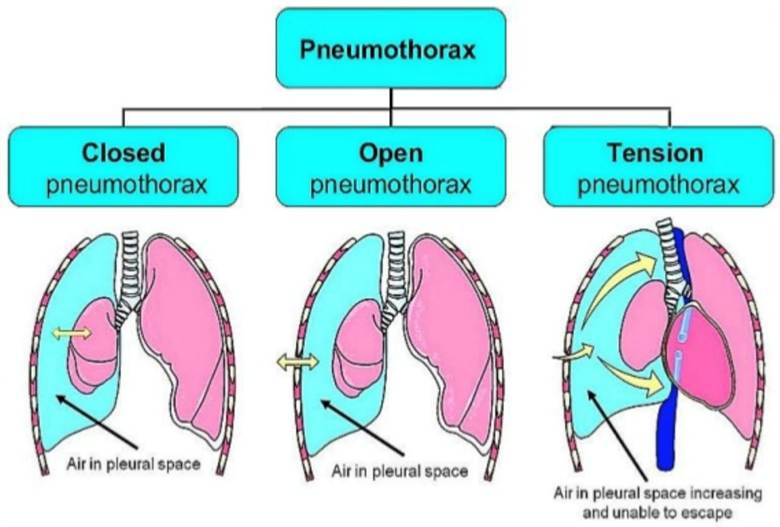
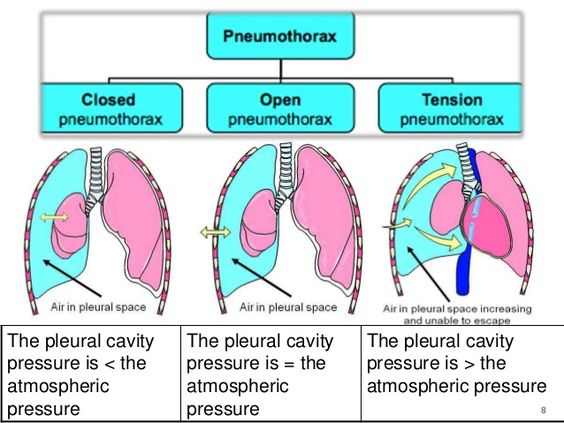
- Closed (Simple) Pneumothorax
- No external wound
- Air from ruptured lung
- Mild to moderate symptoms
- Open Pneumothorax
- Chest wall wound (stab, gunshot)
- Air moves in & out
- Also called sucking chest wound
Note- It is an emergency condition
- Tension Pneumothorax
- Air enters but cannot escape
- Pressure builds rapidly
- Compresses heart & lungs
Rememberable point- Tension = Too much pressure (Life-threatening)
- Spontaneous Pneumothorax
- Occurs without trauma
- Tall, thin males
- Smokers
Causes of Pneumothorax
Traumatic Causes
- Rib fracture
- Stab or gunshot wound
- CPR
- Mechanical ventilation
Non-Traumatic Causes
- COPD
- TB
- Lung disease
- Ruptured blebs
Rememberable point- Sudden chest pain in a tall thin smoker- spontaneous pneumothorax.
Pathophysiology
Cause (Trauma / Spontaneous rupture / Iatrogenic injury)
↓
Air enters pleural space (between visceral and parietal pleura)
↓
Loss of negative intrapleural pressure
↓
Lung recoil inward (elastic collapse of affected lung)
↓
Partial or complete lung collapse
↓
Decreased alveolar ventilation
↓
Impaired gas exchange
↓
Hypoxemia (↓ PaO₂)
↓
Dyspnea, tachypnea, chest pain
If pneumothorax progresses (Tension pneumothorax): –
Continued air entry with no escape
↓
Progressive increase in intrapleural pressure
↓
Severe lung collapse
↓
Mediastinal shift to opposite side
↓
Compression of opposite lung & great vessels
↓
↓ Venous return to heart
↓
↓ Cardiac output
↓
Hypotension → Shock → Cardiac arrest (if untreated)
Clinical Manifestations
General Symptoms
- Sudden chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Anxiety
- Tachypnea
Tension Pneumothorax Signs (VERY IMPORTANT)
- Severe respiratory distress
- Tracheal deviation
- Hypotension
- Jugular vein distension
- Cyanosis
Rememberable point- Tracheal deviation + hypotension = TENSION pneumothorax
Diagnosis
- Physical Examination
- ↓ or absent breath sounds (affected side)
- Hyperresonance on percussion
- Asymmetrical chest movement
- Chest X-ray- Visible air in pleural space, Collapsed lung
- CT scan- In Small or unclear cases
Clinical Diagnosis (Tension Pneumothorax)
DO NOT WAIT for X-ray = Treat immediately
Medical Management
- Simple Pneumothorax
- Oxygen therapy
- Observation (small cases)
- Needle Decompression– Emergency for tension pneumothorax
Insert needle:
- 2nd intercostal space
- Mid-clavicular line
Purpose: release trapped air
- Chest Tube Insertion
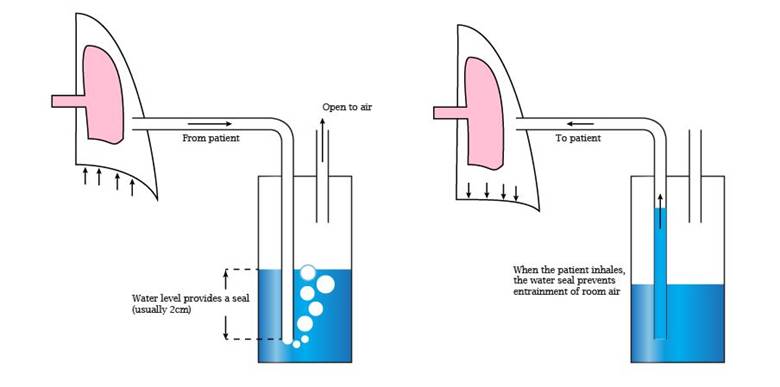
- Removes air
- Re-expands lung
- Connected to underwater seal
Nursing Management (Chest Tube Care)
- Ensure tube is not kinked
- Keep drainage system below chest level
- Observe for bubbling (air leak)
- Assess respiratory status frequently
Dietary Management
- High-protein diet
- High-calorie foods
- Adequate fluids
Nursing Care Plan (NCP)
NCP 1: Impaired Gas Exchange
Related to: Collapsed lung
Evidenced by: Dyspnea, ↓ SpO₂
Goals:
- SpO₂ ≥ 94%
- Improved breathing
Nursing Interventions & Rationale:
- Administer oxygen
- Increases oxygen availability
- Position in high-Fowler’s
- Maximizes lung expansion
- Monitor ABGs & SpO₂
- Detects hypoxia early
NCP 2: Ineffective Breathing Pattern
Related to: Chest pain and lung collapse
Interventions:
- Encourage slow deep breathing
- Provide pain relief
- Support chest during coughing
NCP 3: Acute Pain
Related to: Pleural irritation / chest tube
Interventions:
- Assess pain scale
- Administer analgesics
- Reassure patient
NCP 4: Anxiety
Related to: Sudden breathlessness
Interventions:
- Stay with patient
- Explain procedures calmly
- Encourage controlled breathing
Pneumothorax vs Hemothorax
| Feature | Pneumothorax | Hemothorax |
| Pleural content | Air | Blood |
| Breath sounds | Absent | Dull |
| Percussion | Hyper resonant | Dull |
| Treatment | Chest tube | Chest tube |