MEGALOBLASTIC ANAEMIA- simple way to prevention
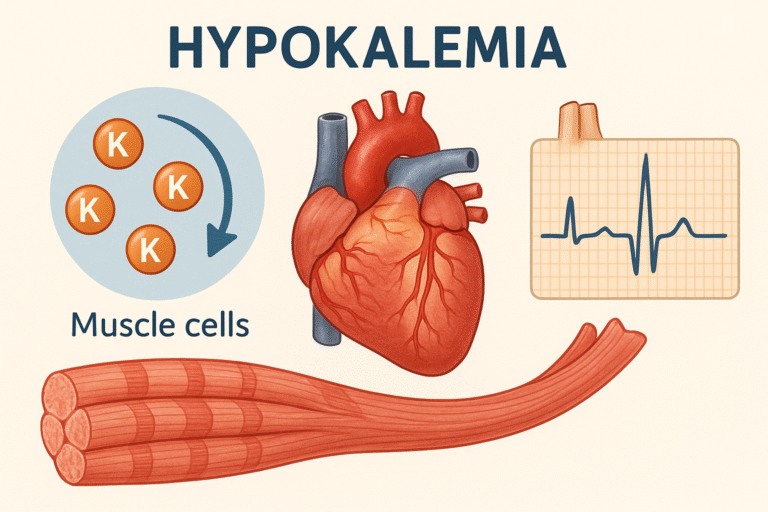
Definition Megaloblastic Anaemia is caused by vitamin B12 or folic acid deficiency which makes RBCs to large, immature, and abnormal which leads to RBCs destruction. Megaloblastic anaemia is a condition in which the red blood cells become larger than normal. Anaemia itself means that the blood does not have enough healthy red blood cells to…