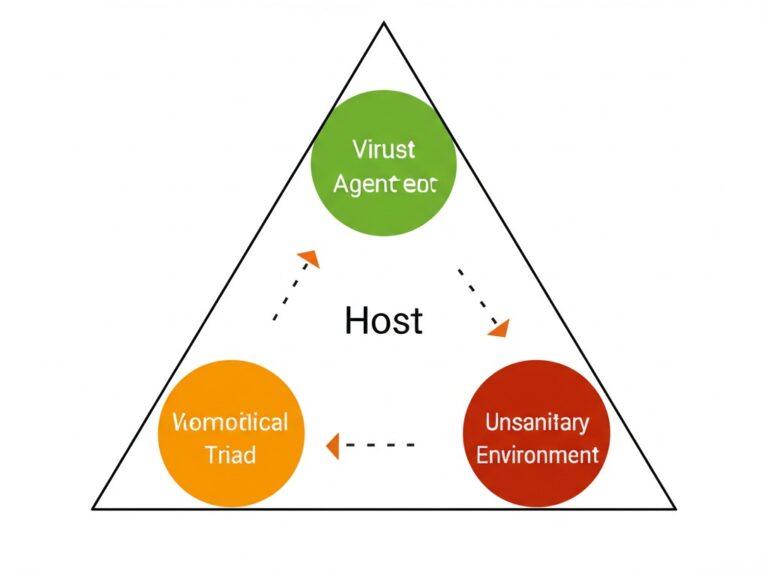
MALARIA- A zoonotic disease caused by mosquito
Causative Agent:
Protozoan parasite Plasmodium
Species:
- Plasmodium vivax – Most common in India
- Plasmodium falciparum – Most dangerous; causes cerebral malaria
- Plasmodium malariae
- Plasmodium ovale
- Plasmodium knowlesi – Primarily in monkeys; rare in humans
NOTE; – 25th April: World Malaria Day
1-30th June: Anti—Malaria Month
Vector:
Female Anopheles mosquito (bites mainly at night)
Historical Discoveries
- Transmission by mosquito: Discovered by Ronald Ross
- Malarial parasite discovered by: Charles Alphonse Laveran
Symptoms
Typical Symptoms:
- High fever with chills and sweating
- Headache
- Muscle pain and fatigue
- Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea
Severe Symptoms:
- Cerebral malaria (coma)
- Severe anemia
- Multi-organ failure
Diagnosis
| Method | Notes |
| Microscopic Blood Smear | Gold standard for diagnosis |
| RDTs (Rapid Diagnostic Tests) | Useful in field conditions |
| PCR | For species-specific identification |
Prevention & Control
- Use of insecticide-treated bed nets (ITNs)
- Antimalarial prophylaxis for travelers
- Elimination of stagnant water (mosquito breeding sites)
Treatment
- P. falciparum: Artemisinin-based Combination Therapy (ACT)
- P. vivax: Chloroquine + Primaquine (Primaquine prevents relapse)
- Pregnancy (Drug of Choice): Chloroquine
- Complicated/Severe Malaria: Intravenous Artesunate